Electronic Throttle Body: Symptoms, Testing, Problems, Replacement
January 08, 2023 By Vlad Samarin
 Electronic Throttle Body. Larger photo
Electronic Throttle Body. Larger photoIn modern cars, the throttle body is electronically controlled. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal the sensors in the pedal send the signal to the engine computer or PCM. The PCM (Powertrain Control Module) commands the electronic throttle body to open the throttle valve accordingly.
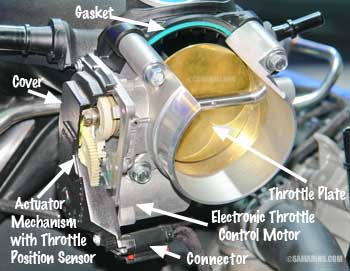 Electronic Throttle Body. Ford cutaway display. Larger photo
Electronic Throttle Body. Ford cutaway display. Larger photoA typical throttle body has a small electric motor that opens or closes the throttle valve using a gear drive. In many modern cars, there are two throttle position sensors built within the throttle body. Throttle position sensors (TP1 and TP2) provide feedback to the PCM of the throttle valve angle.
In modern cars, the electronic throttle body also controls the engine idle speed. When the engine idles, the throttle valve remains open at a small angle, allowing a small amount of air to enter the engine.
Symptoms of Electronic Throttle Body Problems
- Electronically reduced engine power (limp home mode)
- Throttle or wrench warning light, Traction Control light stays ON on the dash
- Abnormal buzzing or repeated clicking noises from the throttle body when the ignition is turned ON.
- Check Engine light stays ON with codes related to the throttle body or idle (e.g., P2100, P2101, P2110, P2111, P2112, P2118, P2135)
- Too low or too high or unstable idle speed
- Stalling at low RPMs
Electronic Throttle Body Problems
One common problem is when an internal fault within the throttle body causes the engine to go into fail-safe or limp mode. It could be a problem with one of the throttle position sensors or with the throttle valve electric motor or the gear drive. When this happens, the Check Engine light, the Traction Control warning light and the Throttle warning light may also come on. In some cars, the Wrench light may come on. In a limp mode, engine power is limited electronically. Often, when the engine shut down and restarted, it may run normally until the problem re-occurs again. Common Check engine light trouble codes (DTCs) related to the throttle body are: P2101, P2110, P2112, P2118, P2135.Another common problem is when carbon deposits accumulated around the throttle valve restrict the air flow causing problems with the idle. Often this happens after the battery has been disconnected or replaced. If the throttle body is dirty, the vehicle may stall or the idle speed can be too low or too high or fluctuate up and down.
Excessive carbon buildup within the throttle body can also cause the throttle valve to bind or stick. This in turn can also cause the car to go into a limp mode and the trouble codes related to the throttle body.
Throttle Body Testing
Testing the throttle body is a relatively simple process, but it needs to be done according to the manufacturer's guidelines. The electronic throttle body can open or close the throttle valve with a considerable amount of torque. To prevent injury, be careful to keep fingers away from the throttle mechanism when it's activated.The first step typically involves a visual inspection and checking the basics: Is the battery voltage within specs? Low battery voltage can also cause throttle body faults. Is the throttle body connector tight? Are there signs of corrosion or damage to the throttle body connector or wire? Are there any objects or excessive carbon buildup within the throttle body that could prevent the throttle valve from opening and closing freely?
If there is a problem with the throttle body, the Check Engine light will most likely be on. The next step is to have the vehicle scanned for trouble codes. If you don't have a scan tool, there are several apps that you can install on your phone that can scan your car for codes. You will need a wireless or Bluetooth OBDII adaptor.
Some auto parts stores can scan your vehicle for free. Once you know the code, check for service bulletins issued by car manufacturers related to that trouble code. If you don't have access to the factory service manual, google the trouble code along with the Make, Model and Year; many service bulletins are published online.
We also have a list of websites where for a fee you can get access to factory service manuals at the bottom of this article.
For example, we found the service bulletin SB-10044229-8347 for a number of Chevy and GM vehicles with the code P2135: Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 1-2 Correlation. This is a pretty common problem in some GM trucks. The bulletin recommends repairing the throttle body with the Sensor Kit for this code and for some vehicles, to reprogram the PCM. We recommend getting this repair done at your GM dealership as it requires quite a bit of skill and precision.
In some cases, car manufacturers extend the warranty for the throttle body if it's a known problem. For example, Ford issued the Customer Satisfaction Program 13N03 that extended the warranty for the throttle body in some cars.
If there are no service bulletins, next, the throttle body needs to be inspected/tested according to the manufacturer's guidelines. Manufacturers provide diagnostic steps for each trouble code.
If you have a scan tool, it's fairly easy to test the throttle position sensor. In some cars, the scan tool can show one signal for throttle position sensor, in others you can check both throttle position sensors TP1 and TP2. Make sure there are no cuts or spikes in the voltage signal.
Here, we checked the throttle position sensor voltage with the Torque app. As you can see the signal is stable and has no spikes. If the signal of either of the sensors cuts out or spikes, the sensor is bad and the throttle body needs to be replaced (unless repair parts come separately).
When the throttle body is removed, you can check the resistance of the TP sensors according to the wiring diagram. If the sensors are OK, the resistance of the throttle body motor also needs to be checked to make sure it's within specs.
When the throttle body removed, the throttle valve needs to be inspected for signs of sticking or binding or excessive carbon buildup. The plastic gears are common to fail and cause the throttle valve to bind. For example, in some Jeep 2.4L engines, the gear teeth are common to wear out and cause the throttle body to fail
If the repair parts are not sold separately, a failed throttle body will need to be replaced.
Throttle Body Cleaning
 Dirty Throttle Body. Larger photo
Dirty Throttle Body. Larger photoCleaning the throttle body is a delicate procedure and needs to be done according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Certain types of cleaners can damage the electric components, seals and O-rings and wash off the grease from the shaft bearings.
Mechanics typically use a special carb cleaner spray and a small plastic brush or towel to clean the throttle body. Watch these Youtube videos. In many cars, after cleaning the throttle body, the idle re-learn procedure will need to be performed.
Throttle Body Replacement
 New Throttle Body. Larger photo
New Throttle Body. Larger photoThe labor charge to replace a throttle body varies from 0.5 to 1.0 hour for most cars. The new OEM throttle body (part) is quite expensive (several hundred dollars).
If your car is recently out of warranty and the throttle body has failed, it makes sense to request the dealer to apply for goodwill coverage or contact the manufacturer directly. We know cases where the car manufacturers covered such repairs out of warranty.
Aftermarket parts are cheaper but the quality is not consistent. If you opt for an aftermarket part, look for a premium-quality part, check the ratings and reviews.
The throttle body gasket is typically replaced together with the throttle body. If after replacing the throttle body the engine idle speed remains unstable or too high, search for the idle re-learn procedure for your vehicle. It might include simple steps such as leaving the ignition ON for a short time and then letting the engine idle for some time. We found several Youtube videos describing this procedure for different cars.
