Home How car parts and sensors work
How car parts and sensors work
Articles:
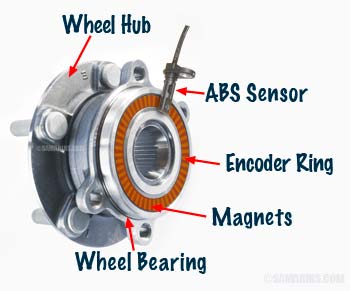
ABS sensor
The function of the ABS sensor is to measure the rotational speed of the wheel. There are four ABS sensors in a car; one at each wheel. n technical literature the ABS sensor is known as Wheel Speed Sensor or WSS.

Air fuel ratio sensor
The air-fuel ratio sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust and provides feedback to the engine computer. Based on that feedback, the computer adjusts the air to fuel ratio by varying the amount of injected fuel.
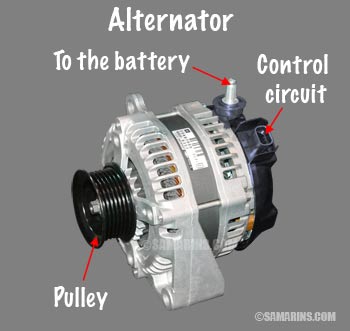
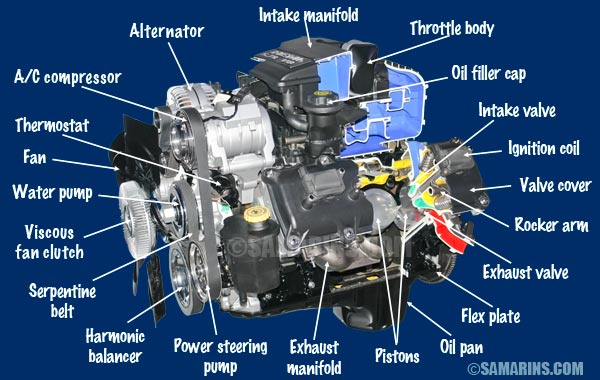
Alternator
The alternator is attached to the engine and is driven by a drive belt. When the engine is running, an alternator generates electric power to recharge the battery. An alternator doesn't need any maintenance, but it can fail and will need to be rebuilt or replaced.

Battery Sensor
The battery current sensor measures the electric current to and from the battery. It may also monitor the voltage, state of charge, state of health (aging) and the temperature of the battery. Most cars have one battery sensor installed at one of the terminals.
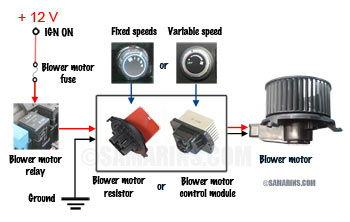
Blower Motor Resistor
The blower motor resistor is the part that controls the speed of the blower motor in the manual HVAC system. One of the symptoms of a failed blower motor resistor is when the blower motor works only at the highest speed setting.

Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter or "cat" is a key component of the vehicle emission control system. It reduces harmful emissions coming out of exhaust. The catalytic converter is built inside the exhaust manifold or within the exhaust pipe close to the exhaust manifold.

Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch serves two major functions. First, it turns on the brake lights when a driver presses the brake pedal. Second, it sends the signal to the vehicle computer that brakes are applied.

Check Engine Light
When there is a fault with one of the vehicle's emission control systems or sensors in the car, the Check Engine light indicates that the trouble code is stored in its memory. There are hundreds of possible trouble codes.

Clock Spring
The clock spring's function is to maintain a stable electrical connection in any steering wheel position and while turning. A car with a faulty clock spring is unsafe to drive as the horn and the driver's airbag may not work.
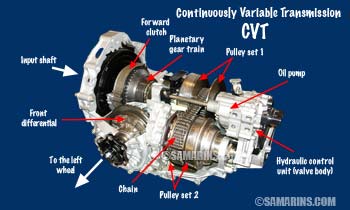
Continuously Variable Transmission CVT
The concept of a continuously variable transmission or CVT is based on a chain that runs between two pulleys. By varying the size of the pulleys, the CVT transmission changes the "gear ratio" gradually.
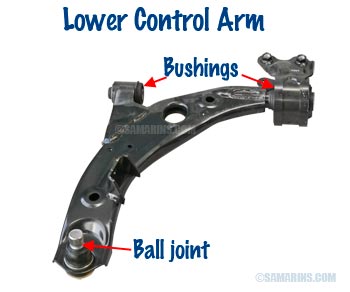
Control Arm
One of the main components of the front suspension, the control arm connects the front wheel to the vehicle's chassis. In many cars, a ball joint is built into the control arm as one piece.
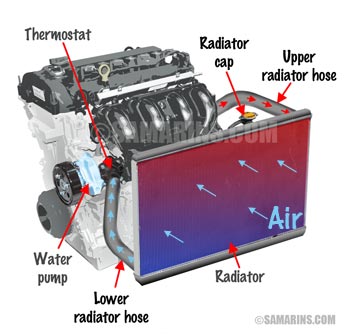
Cooling System
The cooling system keeps the engine from overheating. The system is filled with liquid coolant (antifreeze) and is connected into a loop with the radiator. The coolant flows through the engine absorbing the heat and releases it while flowing through the radiator.

Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor measures the rotation speed (RPMs) and the precise position of the engine crankshaft. Without a crankshaft position sensor the engine wouldn't start. In some cars, the sensor is installed close to the main pulley (harmonic balancer).
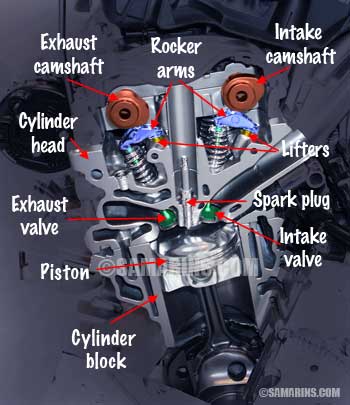
DOHC Engine
DOHC means Double Over Head Cam, or sometimes it could be called "Twin Cam" or "Double Cam." It means that the valves in an engine are operated by two (intake and exhaust) camshafts. Most modern cars have DOHC engines.
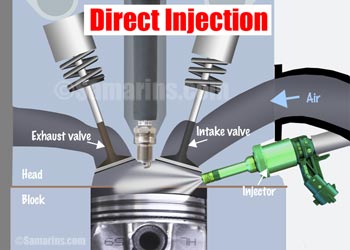
Direct Injection (gasoline)
In an engine with a gasoline direct injection (GDI), fuel is sprayed under very high pressure directly into the combustion chamber. It's different from multi-port fuel injection where fuel injectors spray the fuel into the intake manifold.
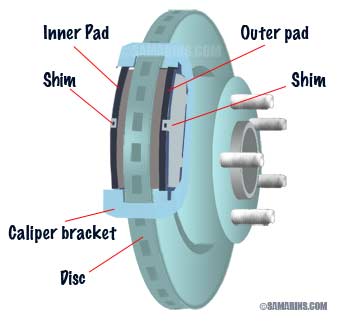
Disc Brakes Diagram
How disc brakes work: when you press the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure of the brake fluid pushes the piston out of the brake caliper. The caliper operates the brake pads that squeeze the disc between them, forcing it to stop.

Door Lock Actuator
The door lock actuator is an electrically-powered device that operates the door latch and power lock mechanism. In many cars, the door lock actuator is built with the latch mechanism into one assembly. Each door has one door lock actuator.
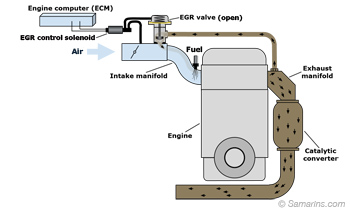
EGR System
As a part of the vehicle emission controls, the Exhaust Gas Recirculation or EGR system helps reducing the amount of the nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the exhaust gases. It does that by reducing the combustion temperature by diverting a portion of the exhaust gases back into the intake manifold.

EGR Valve
The Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system redirects a small amount of exhaust gases back into the engine intake to reduce the combustion temperature. The EGR valve is the main component of this system. By opening and closing It controls the flow of exhaust gases within the EGR system.

Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
The engine cooling system maintains the optimal temperature of the engine and prevents it from overheating. An engine coolant temperature sensor or ECT measures the temperature of the liquid coolant.

Engine Mount
The engine mount is the part that helps holding the engine in its place. In most cars, an engine and transmission are bolted together and held in place by three or four mounts. The mount that holds the transmission is called the transmission mount, others are referred to as engine mounts.

Fuses
Fuses protect electric circuits in a car from overloading. Each circuit has its own fuse. Larger fuses with high Amp rating protect multiple or high-current circuits. There is also at least one main fuse.

Horn in a car
The horn in a car is a safety device. If it doesn't work, the vehicle is deemed unsafe to drive. Problems with the horn in a car not working at all or sounding distorted are common. However, the electric circuit that controls the horn is fairly simple.

Ignition Coil
The ignition coil is a part of the vehicle's ignition system. It converts the 12V battery power into high voltage in order to create a spark at a spark plug. The spark ignites the air/fuel mixture in the engine cylinders.
Most modern cars have one ignition coil per cylinder.

Intake Manifold
The intake manifold in a car is the part of the engine that distributes the air flow between the cylinders. Often an intake manifold holds the throttle valve (throttle body) and some other components. An intake manifold consists of the plenum and runners.

Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
The mass air flow sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. This measurement is used by the engine computer to calculate the amount of injected fuel. The mass airflow sensor is installed between the intake manifold and air filter.
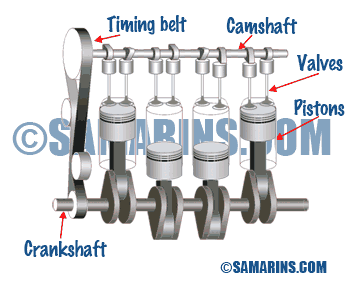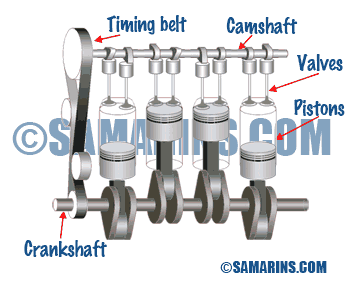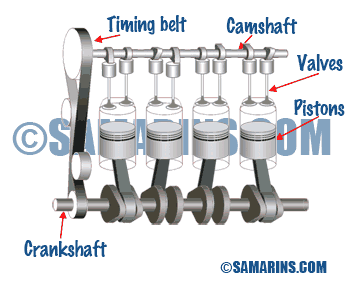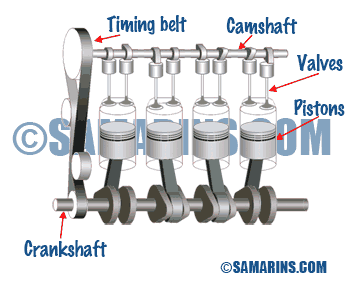
OHC or SOHC Engine
The acronym OHC means Over Head Cam, while SOHC means Single Over Head Cam or Single Cam. In a SOHC engine the camshaft is installed in the cylinder head, and valves are operated either by the rocker arms or directly through the lifters.
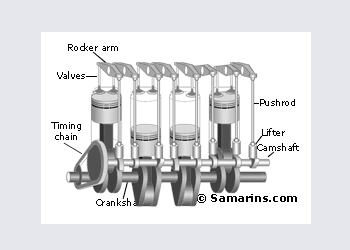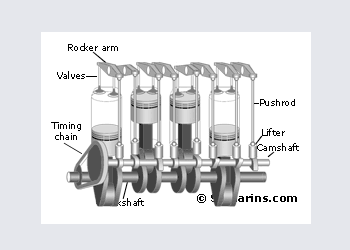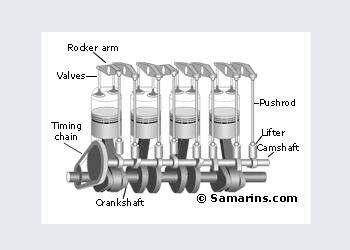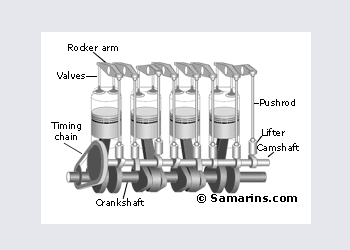
OHV Engine
Over Head Valve or OHV engine is also called a "Pushrod" engine. In this design the camshaft is installed inside the engine block and valves are operated through lifters, pushrods and rocker arms.

Oil pressure sensor (switch)
The oil pressure sensor (switch) is a vital component of any car engine. It is usually installed in the cylinder block close to an oil filter or at the oil filter housing. The oil pressure sensor monitors the engine oil pressure.

Outer tie rod end
The outer tie rod end is an important component of a car's steering system. It connects the steering gear (steering rack) to the steering knuckle, which is the part that holds the front wheel.

Purge Valve
The Evaporative Control (EVAP) system traps fuel vapors from the fuel tank and stores them in the charcoal canister. The purge valve controls the flow of the fuel vapors from the charcoal canister.

Serpentine Belt
The serpentine belt runs the accessories such as an alternator, power steering pump, water pump and air conditioner compressor. Over time, a serpentine belt wears and must be replaced.
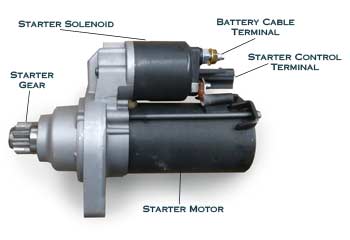
Starter Motor
A starter is an electric motor that turns over or "cranks" the engine to start it. To turn over the engine the starter motor requires a very high electric current, which means the battery has to have sufficient power.

Steering U-joint
The steering u-joint has four needle bearings packed with grease and sealed. A failed steering u-joint could cause a knocking noise in the steering. The steering also could become stiffer at certain angles.

Thermostat
The thermostat is an important part of the engine cooling system. It helps the warm the engine up faster and maintain the proper operating temperature. One of the symptoms of a bad thermostat is lack of heat when driving on a highway.

Throttle Body
In a gasoline engine, the engine speed is controlled by the amount of air that enters the engine. The part that controls the amount of air entering the engine is called a throttle valve. The throttle valve is installed within the throttle body.

Timing Belt
The timing belt connects the engine crankshaft with the camshaft(s) to "time" the opening and closing of the valves with the movement of the pistons. The belt wears out over time and must be replaced in the recommended intervals.

Transmission Range Switch
In cars with an automatic transmission, the transmission range switch allows the starter operation only when the transmission is in Park or Neutral. The transmission range switch monitors which gear the transmission is in.
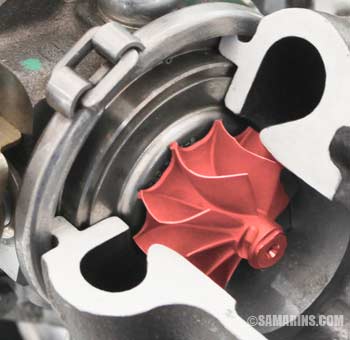
Turbocharger
The turbocharger allows for a smaller engine for better fuel economy and kiks in for extra power when needed (e.g., when passing or merging). Using the energy of exhaust gases, the turbocharger pumps more air into the engine intake under pressure.

Vacuum leaks
What is a vacuum leak?
It's a leak anywhere between the engine and a mass air flow sensor. A vacuum leak causes "unmetered" air to enter the system. Symptoms of a vacuum leak include the Check Engine light, rough idle, stalling and a hissing sound coming from the engine bay.

Vent Valve, EVAP system
All modern cars are equipped with an Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from the fuel tank from escaping into the atmosphere. The EVAP vent control valve (solenoid), or vent valve, is a part of the EVAP system.

Window Motor
The window motors operate power windows in your car. A window motor is installed inside the door and works together with a window regulator to raise and lower the window. In some cars, a window motor can be replaced separately, in others it comes with the window regulator as a unit.
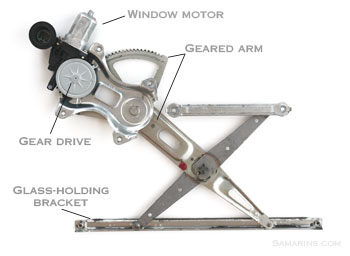
Window Regulator
The window regulator works with a window motor to slide the window up and down inside the door. A bad window regulator can cause the window not to open or close fully or produce irregular noises when the window is operated. If it fails, the failed part or the whole unit must be replaced.

Windshield washer fluid pump (motor)
The windshield washer system is fairly simple: there is a switch, the control module and the motor. The pump comes with the motor as one unit. In some older cars the switch powers the pump directly. The windshield washer motor/pump is installed at the windshield washer fluid bottle.
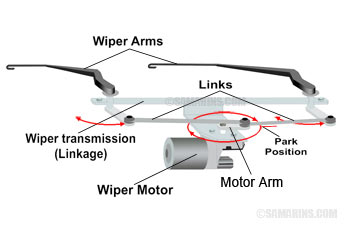
Wiper Linkage (transmission)
The wiper linkage is the frame that holds the wiper motor, wiper arms, and links that connect the wiper motor to the arms. In most cars, the wiper linkage is hidden under the cowl panel cover.

Wiper Motor
The wiper motor is a DC (direct current) 12V motor that includes set of gears and a park switch. The park switch allows the motor to stop when wipers are positioned at the bottom of the windshield. This position is called "park position".